Alaska |
|
|
|
| Übersicht – Contents: | |
Diese Seite ist Teil des Projektes
Flagge – Flag: |
|
 |
seit/since 1927, Landes- und Staatsflagge – civil and state flag, Seitenverhältnis – ratio 125:177, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN), 50states.com, Corel Draw 4   |
historische Flaggen – historical Flags: |
|
 |
1799–1818, Flagge der Russischen Amerika Compagnie – Flag of the Russian-American Company, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (EN) |
 |
1818–1867, Flagge der Russlands – flag of Russia, Seitenverhältnis – ratio = 2:3, Quelle/Source, nach/by: Wikipedia (DE)   |
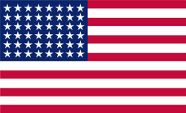 |
1912–1959, Nationalflagge der USA – national flag of the USA, Quelle/Source, nach by: Corel Draw 4 |
| Die Flagge von Alaska ist im Jahre 1926 aus einem Flaggenwettbewerb hervorgegangen. Am 02.05.1927 wurde sie inoffiziell eingeführt. Alaska übernahm diese Flagge im Jahre 1959 auch für den amtlichen Gebrauch. Das Blau steht für den Himmel, das Meer, die Bergseen, und Alaskas Wildblumen. Sieben goldene Sterne stellen das Sternbild Großer Bär (Großer Wagen) dar, welches auch Großer Löffel genannt wird. Der Achte Stern in der äußeren Oberecke ist der Nordstern. Er steht für Alaska den nördlichsten Staat der USA, aber er ist auch der Fixstern der Orientierung gibt. Die Farben sind in den "Alaska-Statuten der Alaska-Staats-Legislative" festgelgt, auch als HEX-Werte, Navy-Blau = #0F204B, Gold = #FFB612. Daraus lassen sich Pantone-Farbwerte ableiten: Blau = pt 655 c, Gelb = pt 1235 c. |
The flag of Alaska
emerged from a flag competition in 1926. It was unofficially introduced on
2nd of May in 1927. Alaska also adopted this flag for official use in
1959. The blue symbolises the sky, the sea, the mountain lakes and Alaska's
wildflowers. Seven golden stars represent the constellation of the Big
Dipper, also known as the Big Bear or Big Carriage. The eighth star in the
outer upper corner is the North Star. It stands for Alaska, the northernmost
state in the USA, but it is also the fixed star that provides orientation.
The colours are defined in the "Alaska Statutes of the Alaska State Legislature", also as HEX values, Navy Blue = #0F204B, Gold = #FFB612. Pantone colour values can be derived from this: Blue = pt 655 c, Yellow = pt 1235 c. |
| Quelle/Source: Flags of the World, Wikipedia (EN) | |
|
Landkarte der Bundesstaaten der USA – Map of the federal states of the USA: interaktiv – clickable |
|
|
Landkarte des Landes – Map of the Country:
Größere Karte anzeigen – View larger map Keine Karte? No map? → |
| Zahlen und Fakten – Numbers and Facts: | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ca. 14.000 v.Chr. · Besiedlung durch Vorfahren der Indianer 1648 · der russische Seefahrer Deschnew durchquert die Beringstraße 1725 · Vitus Bering, dänischer Kartograph und Entdecker in russischen Diensten, erkundet die arktische Küste Sibiriens und Teile der nordamerikanischen Küste, dabei kartiert er die Aleuten-Inseln 1741 · der Kapitän Alexeij Iljitsch Tschirikow, ein Teilnehmer der Bering-Expedition, erreicht Alaska in der Nähe des heutigen Sitka 1759 · der russische Seefahrer Entdecker und Pelzjäger Stepan Glotow landet im Gebiet der heutigen Stadt Unalaska auf den Aleuten 1768 · Unalaska wird ein russischer Handelshafen 1774, 1791 · spanische Expeditionen, Spanien erhebt einige Jahre lang Anspruch auf Alkaska 1775 · die russische Kaiserin Katharina II. (Katharina die Große, 1729–1796), beautragt den sibirischen Kaufmann und Pelzhändler Grigori Iwanowitsch Schelichow (1747–1795) mit der Organisation einer Reihe von Erkundungsreisen zu den Kurilen-Inseln und den Aleuten-Inseln 1778 · britische Forschungs-Expedition des James Cook 1784 · Schelichow gründet in der Three Saints Bay auf der Kodiak-Insel in Alaska eine erste dauerhafte russische Siedlung 1784 · Grigori Iwanowitsch Schelichow und Iwan Larionowitsch Golikow gründen die "Schelikow-Golikow-Kompagnie" 1791–1795 · britische Forschungs-Expedition des George Vancouver 1792 · Alexander Baranow von der "Schelikow-Golikow-Kompagnie" verlegt die russische Siedlung von der Three Saints Bay nach Pawlowsk (heute: Kodiak City) 1797 · Gründung der "Vereinigten Amerikanischen Kompagnie" 1799 · die "Vereinigten Amerikanischen Kompagnie" wird zusammen mit der "Schelikow-Golikow-Kompanie" und der "Lebedew-Lastochkin-Kompagnie" zur "Russisch-Amerikanischen Kompagnie" (RAK) unter Alexander Baranow vereint, der russische Zar überlässt Alaska der RAK für zwanzig Jahre 1799 · Baranow gründet Nowo-Archangelsk (heute: Sitka) an der Küste des amerikanischen Festlands und errichtet dort den Sitz seiner Verwaltung 1802–1804 · Baranow befielt militärische Strafexpeditionen gegen Ureinwohner (Tlingit), die sich der Anwesenheit fremder Händler gewaltsam widersetzten 1806 · Nikolai Petrowitsch Rezanow (1764–1807) baut erste Handelsbeziehungen zwischen Russisch-Amerika und Spanisch-Kalifornien auf und erreicht San Francisco per Schiff, Rezanow betreibt das Vordingen der "Russisch-Amerikanischen Kompagnie" in die Gebiete nördlich von Spanisch-Kalifornien 1808 · Nowo-Archangelsk (heute: Sitka) wird Hauptstadt von Russisch-Amerika 1812 · Alexander Baranow und Iwan Kuskow gründen Fort Ross in der kalifornischen Bodega Bay als Handelstützpunkt zur Versorgung von Russisch-Amerika mit Lebensmitteln 1818 · Russland übernimmt selbst die Verwaltung von Russisch-Amerika 1824, 1825 · Grenzverträge zwischen Russisch-Amerika und Großbritannien und den USA 1839 · Johann August Sutter, ein mexikanischer Bürger schweizerischer Abkunft, gründet die Kolonie Neu-Helvetien nordöstlich von San Francisco, im Gebiet der heutigen Stadt Sacramento 1841 · nachdem Fort Ross die Kolonien in Russisch-Amerika nicht mehr mit Lebensmitteln versorgen konnte, wird der Stützpunkt an Johann August Sutter verkauft Herbst 1848 · Sutter verliert Neu-Helvetien im Zuge des kalifornischen Goldrausches 1865 · Sutter gibt das Projekt Neu-Helvetien endgültig auf 30.03.1867 · Russland verkauft Russisch-Amerika (Alaska) an die USA für 7,2 Millionen Dollar 18.10.1867 · die russische Herrschaft endet, Alaska wird an die USA übergeben und als "Department of Alaska" zunächst von der Armee verwaltet 1877 · das Finanzministerium der USA übernimmt die Verwaltung von Alaska 1879 · die Marine der USA übernimmt die Verwaltung von Alaska 1884 · das "Department of Alaska" wird "District of Alaska" mit eingeschränkter Selbstverwaltung 1912 · der "District of Alaska" wird "Territory of Alaska", Selbstverwaltung 03.01.1959 · Alaska wird der 49. Bundesstaat der USA 1990 · Wahlsieg der Alaskan Independence Party (Gouverneur bis 1994) |
|
ca. 14.000 B.C.
· colonization by ancestors of the Indians 1648 · the Russian sailor Deshnyov sees the Bering Strait 1725 · Vitus Bering, Danish cartographer and explorer in Russian service, explores the Arctic coast of Siberia and parts of the North American coast, mapping the Aleutian Islands 1741 · Captain Alexei Ilyich Chirikov, a participant in the Bering expedition, reaches Alaska near present-day Sitka 1759 · Russian navigator, explorer and fur trapper Stepan Glotov lands in the area of present-day Unalaska on the Aleutian Islands 1768 · Unalaska becomes a Russian trading port 1774, 1791 · Spanish expeditions, Spain claims Alaska for several years 1775 · Russian Empress Catherine II. (Catherine the Great, 1729–1796) commissions Siberian merchant and fur trader Grigory Ivanovich Shelikhov (1747–1795) to organise a series of exploratory voyages to the Kuril Islands and the Aleutian Islands 1778 · British research expedition led by James Cook 1784 · Shelikhov establishes the first permanent Russian settlement in Three Saints Bay on Kodiak Island in Alaska 1784 · Grigory Ivanovich Shelikhov and Ivan Larionovich Golikov found the "Shelikhov-Golikov Company" 1791–1795 · British research expedition led by George Vancouver 1792 · Alexander Baranov of the Shelikhov-Golikov Company moves the Russian settlement from Three Saints Bay to Pavlovsk (today: Kodiak City) 1797 · founding of the United American Company 1799 · the United American Company is merged with the Shelikov-Golikov Company and the Lebedev-Lastochkin Company to form the Russian-American Company (RAK) under Alexander Baranov; the Russian tsar cedes Alaska to the RAK for twenty years 1799 · Baranov founds Novo-Arkhangelsk (today: Sitka) on the coast of the American mainland and establishes his administrative headquarters there 1802–1804 · Baranov orders military punitive expeditions against indigenous peoples (Tlingit) who violently resist the presence of foreign traders 1806 · Nikolai Petrovich Rezanov (1764–1807) establishes first trade relations between Spanish California and Russian America, he reaches San Francisco by ship. Rezanov promotes the advance of the Russian-American Company into the territories north of Spanish California 1808 · Novo-Arkhangelsk (today: Sitka) becomes the capital of Russian America 1812 · Alexander Baranov and Ivan Kuskov found Fort Ross in Bodega Bay, California, as a trading post to supply Russian America with food 1818 · Russia takes over the administration of Russian America 1824, 1825 · Border treaties between Russian America and United Kingdom and the USA 1839 · Johann August Sutter, a Mexican citizen of Swiss descent, founds the colony of New Helvetia northeast of San Francisco, in the area of present-day Sacramento 1841 · After Fort Ross is no longer able to supply the colonies in Russian America with food, the base is sold to Johann August Sutter Autumn 1848 · Sutter loses New Helvetia in the wake of the California Gold Rush 1865 · Sutter finally abandons the New Helvetia project 30th of March in 1867 · Russia sells Russian America (Alaska) to the United States for 7.2 million dollars 18th of October 1867 · Russia's reign ends, Alaska becomes handed over to the U.S. as "Department of Alaska", initially managed by the army 1877 · the Ministry of Finance of the United States takes over the management of Alaska 1879 · the Navy of the United States takes over the management of Alaska 1884 · the "Department of Alaska" becomes "District of Alaska" with limited autonomy 1912 · the "District of Alaska" becomes "Territory of Alaska", autonomy 3rd of January 1959 · Alaska becomes the 49th State of the USA 1990 · election victory of the Alaskan Independence Party (governor until 1994) |
| Quelle/Source: Atlas zur Geschichte, Wikipedia (DE), Discovery '97, Shelikhov Golikov Company, Wikipedia, Alexander Andreyevich Baranov, Wikipedia, Unalaska, Wikipedia, Kodiak, Wikipedia, Sitka, Wikipedia, Fort Ross, Wikipedia, www.msn.com/de, Volker Preuß |
| Der Name "Alaska" geht auf das aleutische Wort "Alakshak" zurück, was übersetzt heißt: "Land, das keine Insel ist". Nach einer anderen Überlieferung lautet die Übersetzung: „Land, zu dem der Ozean fließt“. Die Russen machten daraus "Alieska", die US-Amerikaner "Alaska". | The name "Alaska" has its roots the Aleut word "Alakshak" what means translated: "land which is not an island". According to another tradition, the translation means: "land on which the ocean flows". The Russians formed it to "Alieska", and the US-Americans to "Alaska". |
| Quelle/Source: Handbuch der geographischen Namen, Wikipedia (EN) | |